
In Structural Design, we often encountered different load combinations in structural codes. These combinations vary according to its occupancy. But selecting the right load combinations for the project we are designing is a challenge. Newbies are often having a hard time figuring out which is which. Selecting the right combinations without guidance from a senior engineer is a tough task. Even a senior engineer is sometimes confused about what combinations to use in the design. Not using the right one, may result in an under design or over design results. So as a designer proper design load combinations should be taken into considerations. Thanks to the design guidelines or the design criteria of the given project, it will ease the burden of selecting the proper load combinations. But, if the design guidelines can’t be able to guide us on what to choose, the author lists some important checklist and guidelines in choosing the proper load combinations in your design.
1. Differentiate the Code to be Use in the Model
You can narrow down the selection process if you consider this. Each code combinations can be found in different design codes. To start with, it is important to know the different code to use accordingly whether concrete or steel structures. The use of the design codes is depending on the location of the project. This is a very important part of the design but it usually dictates by the local authority. The usual codes we are using are the ASCE-7, IBC, and UBC-97 for the seismic and wind load combinations, ACI 318 and BS8110 for member design not to mention the governing local codes which is available in your area. Each of these codes has recommended load combinations that can be used in the structural model. To know more about different code standard we are using, refer to the previous article Design Code & Standards.
2. Lists Down the Code According to its Use
Once we already identify which code to use in our structural model, it is more helpful to list down the different load combinations according to its category. Usually, load combinations are categorized into working or service limit state (SLS) or ultimate limit state (ULS). But when to use the SLS or ULS should be clear for us. SLS combination is usually considered for deflection and static checks and ULS is for member design considerations. Under these categories, the Gravity, Wind and Earthquake load combinations can be considered. Check out the detailed combination of loads that have been tackled in our previous article Design Load Combinations for further information.
3. Create a Short Code Description when assigning in the Model
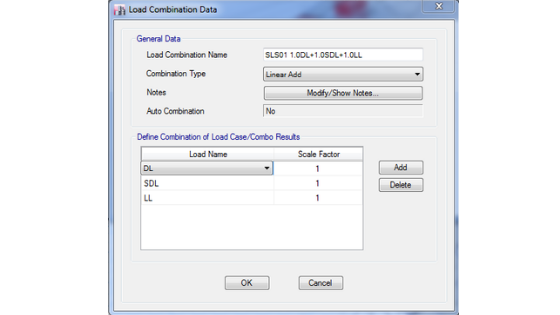
We usually use different Structural Engineering Software in the design analysis. These soft wares usually have limits in load combinations descriptions. So, when applying the load combinations in the model, it is recommended to use shortcode descriptions for us to identify right away the combinations that we assign. Some designers tend to use the full combinations as the descriptions; either way is okay as long as you are comfortable with it. The purpose of making clear descriptions of these load combinations is that to be able to re-track immediately the governing load combinations after the analysis and during design investigations. In this way, we can save a significant amount of time. The figure below taken from ETABS model describes the recommended load combination description.
 4. Apply, Double Check the Assigned Load Combinations and Call a Friend.
4. Apply, Double Check the Assigned Load Combinations and Call a Friend.
For as we are humans, we are prone to make mistakes so it is important to double check each load combinations that we are assigning in the model before any analysis and design. Call a Friend simply means have someone “more experience and senior” to review the code you adopted in the design and let him/her check whether you apply the correct ones if you are in doubt of what you assigned in the model. It would be great if an in-house third-party checker is available to review the said load combinations to save your day.
What do you think of the above this article? Tell us your thoughts! Leave your message in the comment section below. Feel free to share this article, subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on our social media pages.
![]()










