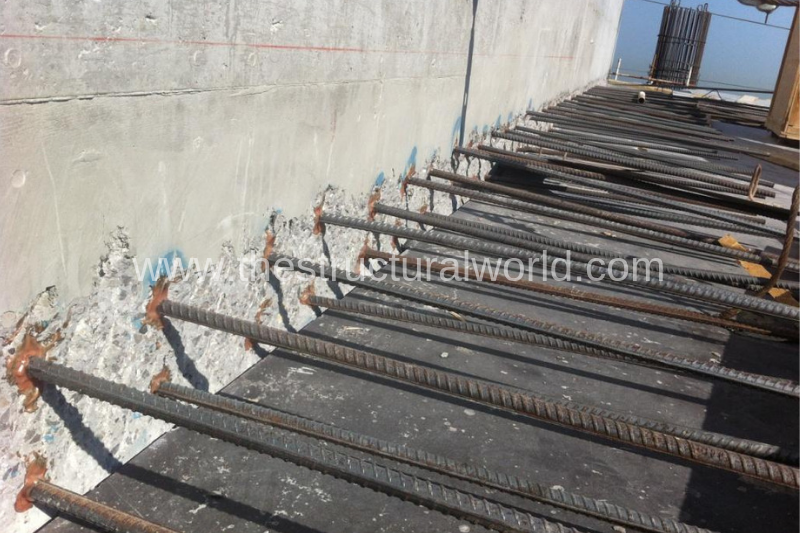

When the construction is in progress, we often encountered unforeseen circumstances in the site that leads to revisions and rectifications. Though the engineering plans and drawing have already been approved for construction, still it is considered as a work in progress until fully constructed. These modifications may be due to client requests, it can be because of further development and design enhancement and structural strengthening. Whatever the reason may be, it can lead to omission or inclusion of structural members.
The most common modification that we encountered during site construction is the addition of structural members to the existing one. In any means, the only way to connect an additional structure from an existing is though drill and fix method. For this, the proper and step by step procedure should be followed by the engineers in order to attain a safe and sound execution.
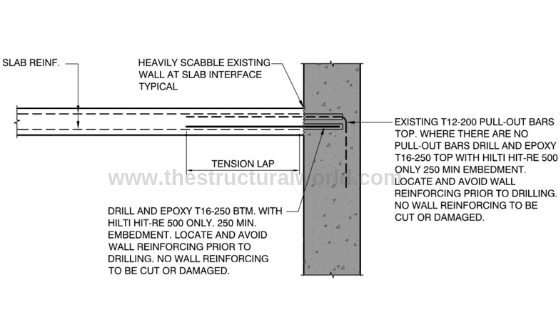
To give you an idea, let us take a look at the example figure below; an additional slab will be fixing to an existing core wall as shown. Refer to the succeeding paragraph for the methodology guide. This method statement for rebar post-fix is a general procedure and may not only apply to the sample detail below but can be also applied to any concrete structure, cast in place or post-tensioned and therefore can be adapted accordingly. Hilti products have been presented in this method statement.
TYPICAL POST FIXED SLAB TO CORE WALL CONNECTION
Method Statement for Post-Fixed Rebar: Drill & Fix with Chemical Anchor
1. Introduction
This method statement covers the step by step procedure and action that the contractor should adopt to undertake rebar drill and fix using chemical anchoring.
2. Scope
The Scope of this method statement covers the various requirements to be provided for preparation like chipping and expose the existing rebar, marking to position the new starter bar location, reconnaissance to confirm and ensure that the existing rebar or PT tendons (in case of PT slab) don’t get disturbed and then do core drilling to required depth.
3. Technical Specification & Reference Details
3.1 Refer to the approved drawing issued by the consultant. Post tension tendon locations as per PT Drawings, and slab/beam, column rebar shop drawings also to be referred.
3.2 Rebar to be fixed is as per the approved design calculation, for example, T16 rebar to be fixing hence use the diameter of the hole to be 20mm (this should be supported by design calculation).
3.3 Hole depth will be a minimum 250 mm. Reference locations of slab inconsideration or proposed and exiting core wall/column rebar is available for consultant review.
4. Materials
4.1 Hilti RE 500
4.2 Rebar (as per approved Project specification)
5. Tools & Equipment
5.1 Heavy duty breakers/jack hammers
5.2 Rotary combination hammer drilling machine
5.3 Hilti coring machine or Equivalent
5.4 A drill bit, coring bit with extension end
5.5 Air blower & compressor machine
5.6 Miscellaneous hand tools
5.7 Surveying equipment
5.8 Dispenser gun for chemical injection
6. General Procedure
6.1 Column set out is done by surveyors & chipping concrete is done with heavy duty breakers till the existing rebar are exposed and the area cleaned.
6.2 Once the location is marked, clearance will be obtained by the contractor prior to the commencement of drilling. The proper safe workplace is ensured and prior necessary coordination is done with MEP.
6.3 Drilling is commenced using for flute spiral drill bit with carbide head. This will ensure smooth drilling and penetration into concrete areas, but won’t disturb rebar.
6.4 Wherever the hole making the procedure as narrated above does not work due to onsite rebar / PT, then the necessary minor shifting of the location is attempted to get clear of the rebar and normal drilling continued.
6.5 In such specific cases where normal drilling is stopped due to rebar / PT, further site reconnaissance is done with available drawings to ascertain the reason for obstruction. The assistance of the coring machine will be utilized to help clear some mirror some minor rebar, after join inspection by contractors and site supervisors.
7. Coring
Prior to coring, confirm water and power connection to the machine are in order. Hilti coring machine is properly anchored to slab with mechanical anchors.S tart 16Ø core drilling to minimal depth to clear the obstacle. Once the specific obstacle like the edge of rebar, etc is cleared, then the coring machine is withdrawn and the area cleaned. Further normal drilling activity reinstated to continue drilling holes to the required depth.
8. Standard Installation Procedure for Post Fixing Rebar
Attached to this submittal is a detailed method statement to be submitted by Hilti for RE 500. This will also include their design calculations which are subjected for consultant approval.
9. Safety
9.1 Work Permits should be obtained prior to starting Work.
9.2 Check proper power supply phase and extension cable condition prior to starting.
9.3 Barricading to be done where ever required.
9.4 Close supervision by the contractor is required during the entire operation.
9.5 Engineer/Supervisor/work in charge should conduct a toolbox meeting and communicate both the Method Statement & Risk Assessment to the workers before the commencement of the activity.
9.6 All safety precautions shall be followed as per the established project safety procedure.
9.7 Only experienced and skilled labor shall be engaged for the job.
9.8 The people involved in the construction work shall wear PPE such as safety helmets, safety shoes, gloves safety glass, mask etc. as required.
9.9 Site supervisor/ engineer & Safety officer shall check and ensure that all safety precautions are followed.
9.10 Manual handling procedures must be followed.
9.11 All electrical tools are to be inspected by the Safety Department prior to use on site.
9.12 Site engineers/ foreman must ensure that the work is carrying out safely.
9.13 COSHH materials to be stored in a dedicated COSHH Store provided at the site.
9.14 MSDS must be followed.
9.15 Any incident or near miss incident shall be reported immediately to the concerned safety officer.
9.16 Third party certified plant and equipment shall be used on site.
9.17 Plant operator must be certified by the third party.
10. Inspections
10.1 Rebar setting out and marking, including PT strands.
10.2 The hole depth and cleaning using a brush and air blower. Contractor to submit for consultant inspection and approval.
10.3 Rebar fixing/application of the chemical.
10.4 Curing
What do you think about this article? Tell us your thoughts! Leave a comment on the section below. Subscribe to our newsletter to be updated with the latest posts or follow us on our social media pages on the below icons.
[DISPLAY_ACURAX_ICONS]










Thanks Article.
Very informative and useful. Please continue issuing this kind of technical matters for referrence. Thank you