
Raft foundation is one of the types of foundation that is composed of a thick mat or slab that supports the entire structures. This type of foundation is used when there are larger column loads to support and when soil bearing capacity is too low. Raft foundations are suitable for medium rise story buildings ranges from four to twelve stories. It can be considered on higher buildings depending if the soil bearing capacity is strong enough to carry the whole structure by examining the generated bearing pressure.
Designing a raft foundation is too complex since a lot of design considerations should be made especially when you are designing a high rise. But thanks to available design software, these complexities narrows down. Perhaps the most popular tool to design a Raft Foundation is through the aid of SAFE program developed by CSI. SAFE is a powerful tool to design simple to complex slabs, pile caps and raft foundations using different specified codes.

Raft Foundation ready for Concrete Pouring
This article will help you through on how to design a raft foundation and their design considerations using SAFE. In designing a raft foundation, load cases and load combinations will be imported from ETABS model and after importing; the modeling and design will take place. The following are the design procedure on how to design a raft foundation using safe.
1. Raft Slab Modeling
Raft modeling is the first step to design a foundation. In modeling, the general arrangement of the foundation has to be reflected. The design loads especially point loads generated by columns above and area load to be carried by the raft should be included. There are two ways to model a foundation in SAFE, either to do it manually and through importing or the combinations of both.
Modeling the raft foundation manually is not recommended for high rise projects since different load considerations generated through the design analysis using ETABS has to be reflected and assigned in the model to make sure that all the load cases and load combinations have been considered. The author recommends importing these loads from ETABS and once imported, model the foundation layout accordingly.
For the designer to import an already analyzed ETABS model, go to File>Import>Safe.F2k File. Note that you need to convert the ETABS model to Safe f2k file, for you to be able to import it to SAFE model. Here is how to create a SAFE f2k file for SAFE Modeling and Design.
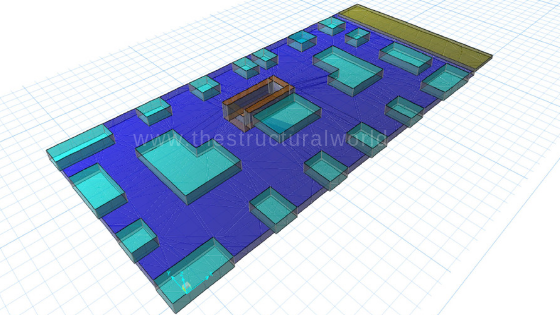 RAFT Foundation with Drop Panel Modeled in SAFE
RAFT Foundation with Drop Panel Modeled in SAFE
2. Design Considerations
After the f2k file has been imported, begin with manually model the Raft general arrangement. Since we imported the model from ETABS, the material properties, load cases and load combinations which were previously defined in ETABS model have been imported as well, so you do not have to worry defining them again. More importantly, the point loads carried by each column, the line loads (if any) and other lateral loads during the analysis have been also imported. The only loads that you need to assign are the area loads composed of super-imposed dead Loads (SDL) and live loads (LL) which the raft will carry. The SDL and LL can be omitted in some cases if no requirement to be added as such.
3. Defining and Assigning Soil Subgrade Properties (ks)
The soil subgrade properties represent how strong the soil bearing pressure will be and it measures the soil pressure capacities per unit settlement (kN/m2/m or kN/m3). To assign subgrade properties, go to Define>Soil Subgrade Properties and define subgrade modulus. The value of subgrade modulus is usually recommended by the geotechnical investigation report available in each project. In the event that subgrade modulus is not available in the soil report, it is safe to assume the subgrade modulus by the following formula based on Foundation Analysis and Design by Joseph E. Bowles pp503:
ks = 40SFqa
Where:
- 40 is constant also equal to 12 when using English units
- SF: safety factor is usually taken as 2.5
- qa: allowable bearing capacity as recommended by soil report
4. Defining Design Strips
Definition of design strips is a very important part in SAFE modeling for raft/mat foundations and slab designs. This is done so that the program will analyze the model according to design strips and interpret accordingly on how much area or number of rebar are required in the strip assign. The recommended one-meter design strips should be defined in x and y directions for convenience. Refer to this video on how to define and assign design strips.
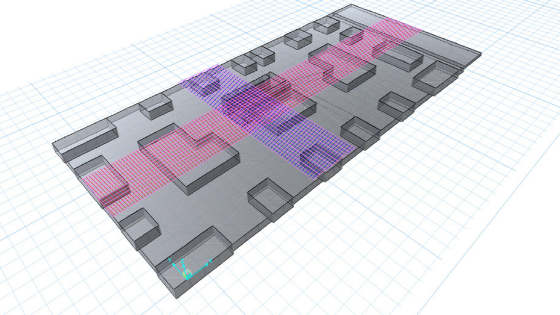
Strips Assignment at X and Y Direction in SAFE
5. Design Preferences
Before running the SAFE model, the designer should review the Design Preferences to use in the model by going to Design>Design Preferences. This window allows you to edit or assign design parameters like the code to be used, minimum concrete covers, etc.
6. Run Analysis and Design
After all the above-mentioned criteria have been set, then you are good to go. For the designer to run analysis and design the raft model, go to Run>Run Analysis and Design. This time, the program will analyze the model according to the parameters that you provided and will display the contour for you to check and investigates the model.
7. Design Check and Review
When the run analysis and design have been completed, the designer should check first the soil pressure generated by the model by going to Display>Show Reaction Forces>Soil Pressure. To compare, hover your mouse pointer into the contour and check the soil bearing pressure. If the soil pressure generated in the model is less than the recommended bearing capacity by the soil report, then it is satisfactory!
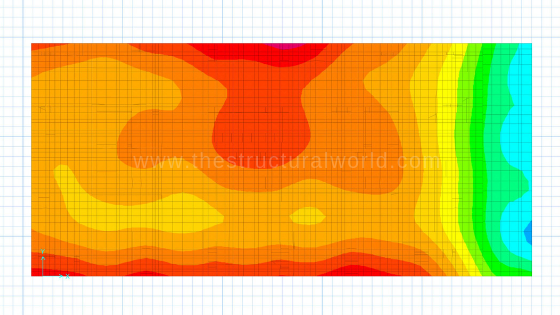
Soil Pressure Diagram Results in SAFE
Punching Shear Check in the model should also be considered to be reviewed. This will see to it if the design loads can withstand by the thickness of the raft. For the model to be checked in punching, go to Display>Punching Shear Design. If the ratio generated is less than unity, then the raft thickness is satisfactory otherwise increase the raft thickness. Refer to this video on how punching shear check can be performed in SAFE.
8. Interpretation of Design Results
Interpreting the result generated by the SAFE program is the last step to do. This is the part where the designer will eventually assign and provide the main mesh top and bottom reinforcement as well as the top and bottom extra bars needed. The reinforcement interpreted will then be reflected on the Raft Foundation Layout Drawings.
The interpretation of SAFE analysis and design of RAFT foundation is similar to slab design. Check out our previous article on how to interpret the slab designs results.
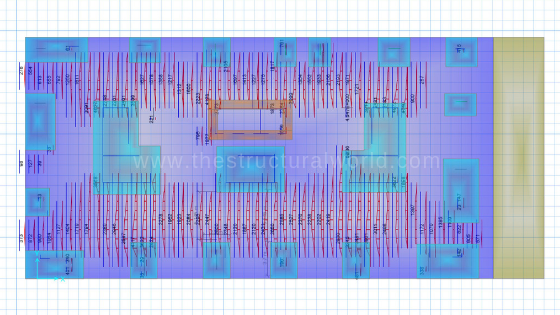
Recommended Reinforcement Results in SAFE
Summary:
Summarizing the above article can be best seen in actual modeling using the SAFE program itself. Check out the YouTube video below how to design a raft foundation using SAFE. Kindly subscribe to our YouTube channel for more structural software tips like this.
What do you think about this article? Tell us your thoughts! Leave a comment on the section below. Subscribe to our newsletter to be updated with the latest posts or follow us on our social media pages on the below icons.
![]()










I want to purchase SAFE software for raft footing design.what is the cost in rupees.
Why is 1 meter design strip recommended?
Shouldn’t it be equal to the depth of raft?
1 meter is recommended because using other widths of design strips requires you to divide the results by the width of the strips you provided in the model to get the actual results. So it’s the same thing.